Abstract
Purpose
Oropharyngeal and tongue exercises (myofunctional therapy) have been shown to improve obstructive sleep apnea. However, to our knowledge, a systematic review has not been performed for snoring. The study objective is to perform a systematic review, with a meta-analysis, dedicated to snoring outcomes after myofunctional therapy.
Methods
PubMed/MEDLINE and three other databases were searched through November 25, 2017. Two authors independently searched the literature. Eligibility (1) patients: children or adults with snoring, (2) intervention: oropharyngeal and/or tongue exercises, (3) comparison: pre and post-treatment data for snoring, (4) outcomes: snoring frequency and snoring intensity, (5) study design: publications of all study designs.
Results
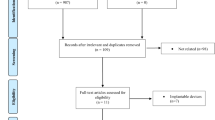
A total of 483 articles were screened, 56 were downloaded in their full text form, and nine studies reported outcomes related to snoring. There were a total of 211 patients (all adults) in these studies. The snoring intensity was reduced by 51% in 80 patients from pre-therapy to post-therapy visual analog scale values of 8.2 ± 2.1 (95% CI 7.7, 8.7) to 4.0 ± 3.7 (95% CI 3.2, 4.8). Berlin questionnaire snoring intensity reduced by 36% in 34 patients from 2.5 ± 1.0 (95% CI 2.2, 2.8) to 1.6 ± 0.8 (95% CI 1.3, 1.9). Finally, time spent snoring during sleep was reduced by 31% in 60 patients from 26.3 ± 18.7% (95% CI 21.6, 31.0) to 18.1 ± 20.5% (95% CI 12.9, 23.3) of total sleep time.
Conclusions
This systematic review demonstrated that myofunctional therapy has reduced snoring in adults based on both subjective questionnaires and objective sleep studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullatif J, Certal V, Zaghi S, Song SA, Chang ET, Gillespie MB, Camacho M (2016) Maxillary expansion and maxillomandibular expansion for adult OSA: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cranio-Maxillo-Fac Surg 44(5):574–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2016.02.001
Camacho M, Certal V, Capasso R (2013) Comprehensive review of surgeries for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 79(6):780–788. https://doi.org/10.5935/1808-8694.20130139
Camacho M, Li D, Kawai M, Zaghi S, Teixeira J, Senchak AJ, Brietzke SE, Frasier S, Certal V (2016) Tonsillectomy for adult obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25931
Riaz M, Certal V, Nigam G, Abdullatif J, Zaghi S, Kushida CA, Camacho M (2015) Nasal expiratory positive airway pressure devices (provent) for OSA: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Disord 2015:734798. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/734798
Certal V, Nishino N, Camacho M, Capasso R (2013) Reviewing the systematic reviews in OSA surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 149 (6):817–829. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599813509959
Certal VF, Zaghi S, Riaz M, Vieira AS, Pinheiro CT, Kushida C, Capasso R, Camacho M (2015) Hypoglossal nerve stimulation in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 125(5):1254–1264. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25032
Kumar AR, Guilleminault C, Certal V, Li D, Capasso R, Camacho M (2014) Nasopharyngeal airway stenting devices for obstructive sleep apnoea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Laryngol Otol:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215114003119
Camacho M, Certal V, Abdullatif J, Zaghi S, Ruoff CM, Capasso R, Kushida CA (2015) Myofunctional therapy to treat obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 38(5):669–675. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.4652
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Baz H, Elshafey M, Elmorsy S, Abu-Samra M (2012) The role of oral myofunctional therapy in managing patients with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. PAN Arab J Rhinol 2(1):17–22
Berreto e Silva Pitta D, Farias Pessoa A, Sampaio AL, Nonato Rodrigues R, Guiot Tavares M, Tavares P (2007) Oral myofunctional therapy applied on two cases of severe obstructive sleep apnea. Intl Arch Otorhinolaryngol 11(3):350–354
Diaferia G, Santos-Silva R, Truksinas E, Haddad FL, Santos R, Bommarito S, Gregorio LC, Tufik S, Bittencourt L (2016) Myofunctional therapy improves adherence to continuous positive airway pressure treatment. Sleep Breath (Schlaf & Atmung). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1429-6
Guimaraes KC, Drager LF, Genta PR, Marcondes BF, Lorenzi-Filho G (2009) Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(10):962–966. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200806-981OC
Ieto V, Kayamori F, Montes MI, Hirata RP, Gregorio MG, Alencar AM, Drager LF, Genta PR, Lorenzi-Filho G (2015) Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on snoring: a randomized trial. Chest 148(3):683–691. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-2953
Kayamori F (2015) The effects of myofunctional and orofascial therapy in patients with primary snoring and obstructive sleep apnea and anatomy and airway function. Doctoral thesis, Faculdade de Medicina, pp 1–116
Nemati S, Gerami H, Soltanipour S, Saberi A, Moghadam SK, Setva F (2015) The effects of oropharyngeal-lingual exercises in patients with primary snoring. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 272 (4):1027–1031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3382-y
Verma RK, Johnson JJ, Goyal M, Banumathy N, Goswami U, Panda NK (2016) Oropharyngeal exercises in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea: our experience. Sleep Breath (Schlaf Atmung) 20(4):1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1332-1
Mohamed AS, Sharshar RS, Elkolaly RM, Serageldin SM (2016) Upper airway muscle exercises outcome in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcdt.2016.08.014 (Epub ahead of print)
Netzer NC, Stoohs RA, Netzer CM, Clark K, Strohl KP (1999) Using the Berlin questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea syndrome. Ann Intern Med 131(7):485–491
Lim PV, Curry AR (1999) A new method for evaluating and reporting the severity of snoring. J Laryngol Otol 113(4):336–340
Friberg D (1999) Heavy snorer’s disease: a progressive local neuropathy. Acta oto-laryngologica 119(8):925–933
Engelke W, Engelhardt W, Mendoza-Gartner M, Decco O, Barrirero J, Knosel M (2010) Functional treatment of snoring based on the tongue-repositioning manoeuvre. Eur J Orthod 32(5):490–495. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjp135
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria, educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required. There is no additional need for informed consent as no identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
The views expressed in this abstract/manuscript are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Army, Department of Defense, or the US Government.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camacho, M., Guilleminault, C., Wei, J.M. et al. Oropharyngeal and tongue exercises (myofunctional therapy) for snoring: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 849–855 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4848-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4848-5